<-Previous Species – Next Species->
Length
35-39mm; Wingspan: Male 42mm; Female 45mm; Hindwing 19-22mm
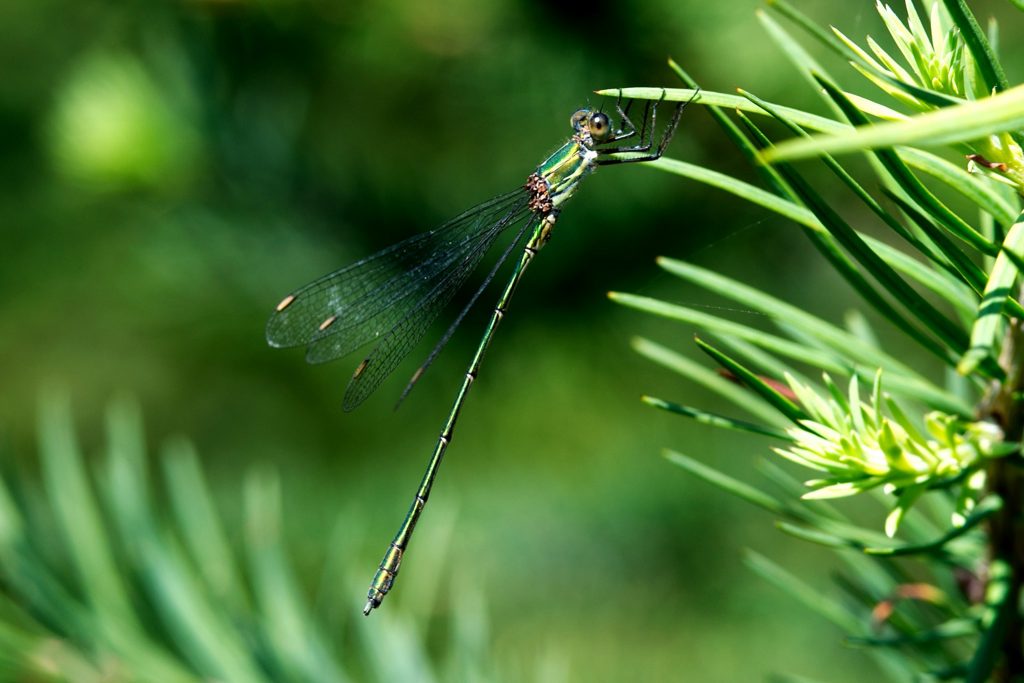
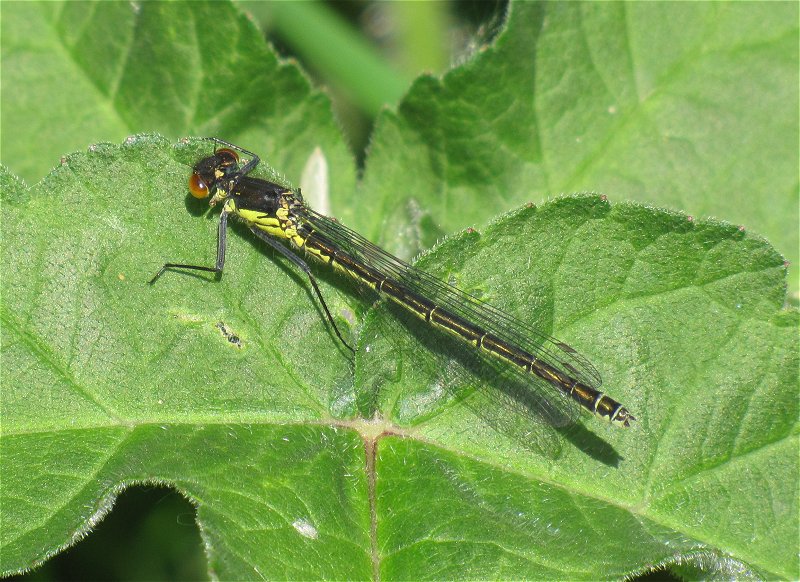
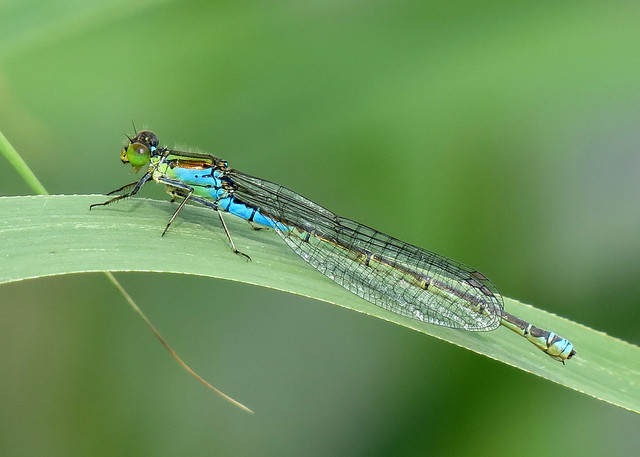
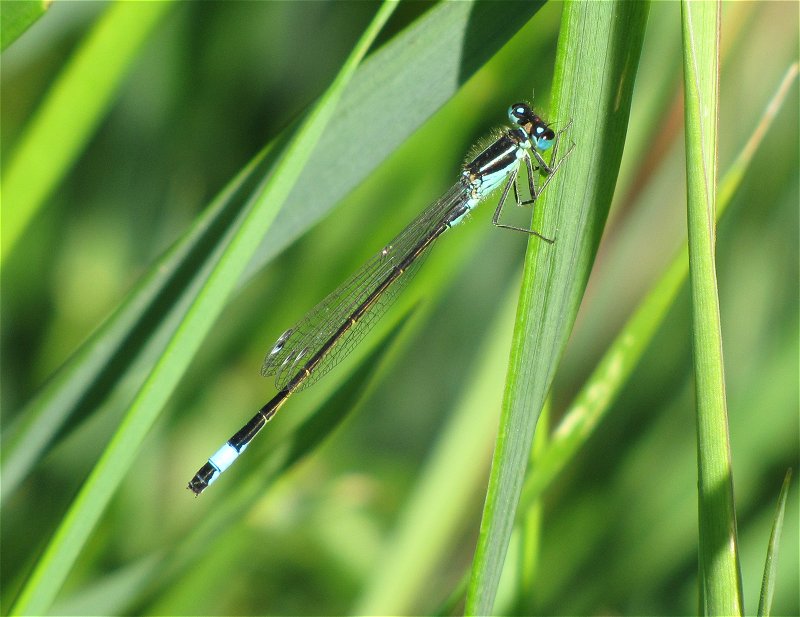
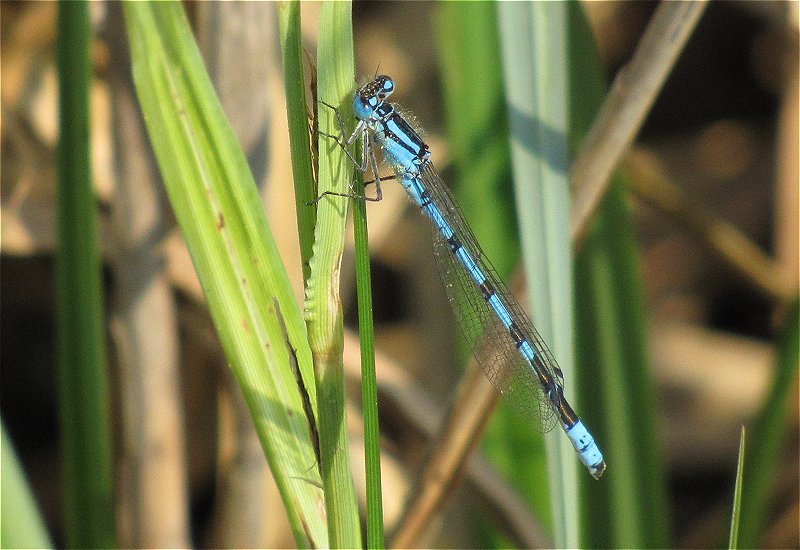
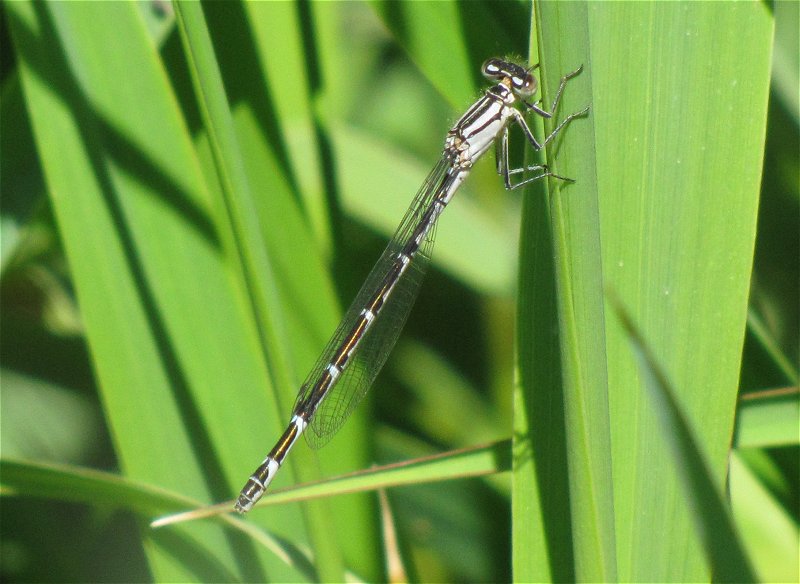
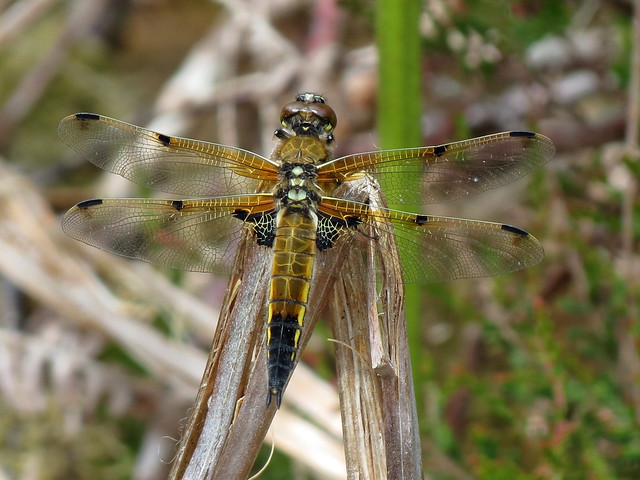
Male

Metallic green in colour. This species has a slow maturation period of two to four weeks, over this period a blue pruinescence appears on the thorax between wings and segments 1,2, 9 and 10. Eyes blue. Confusion species is Scarce Emerald Damselfly which is extinct in Yorkshire. Both sexes rest with wings half open.
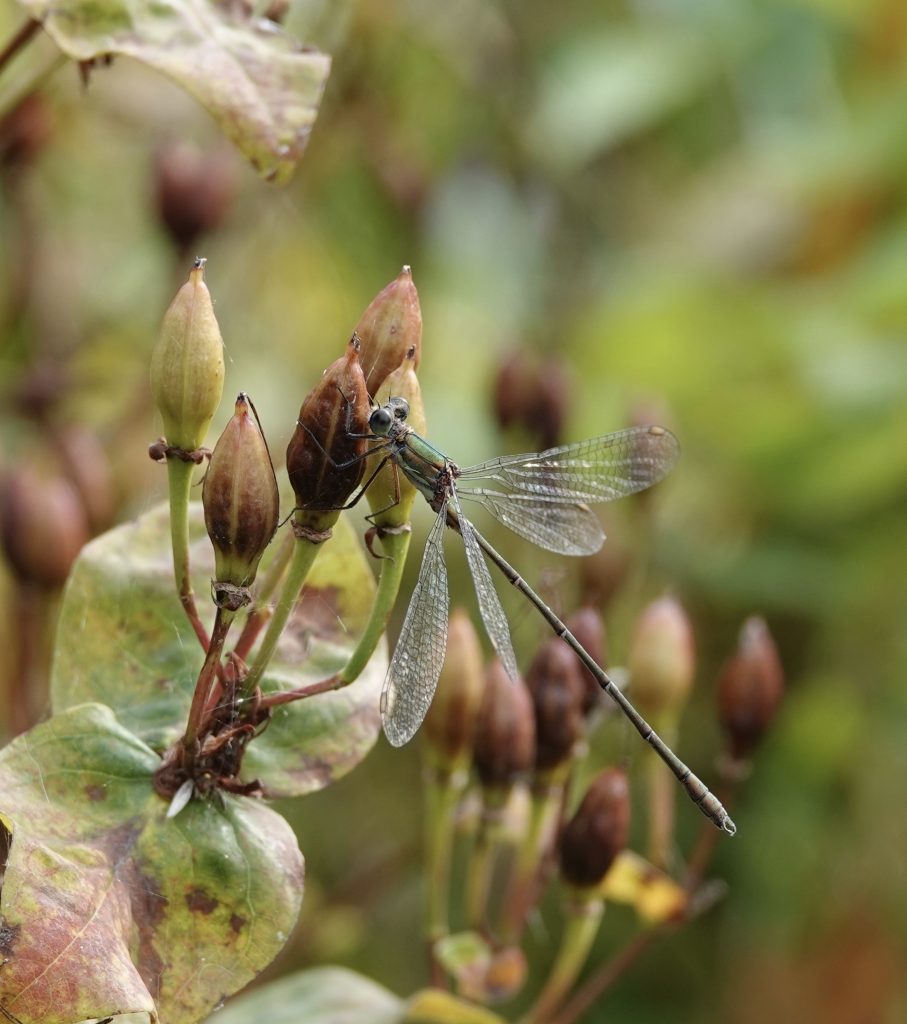
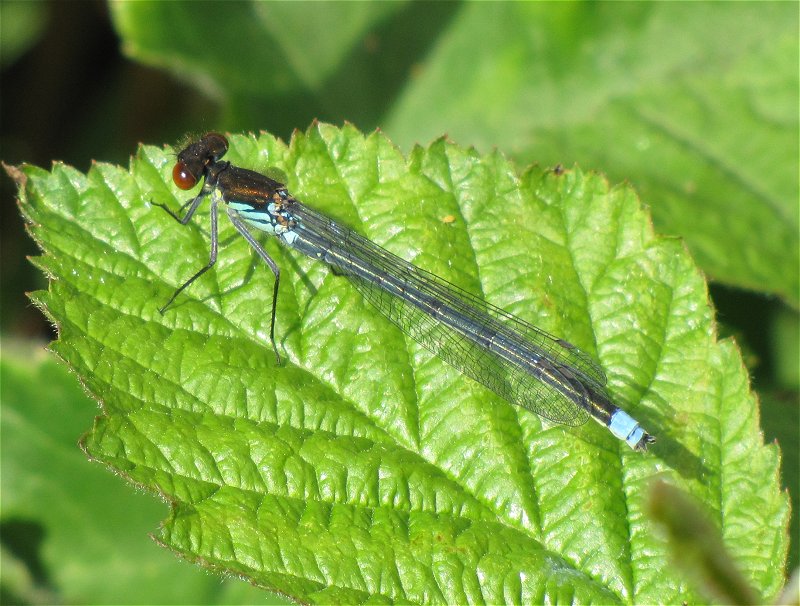
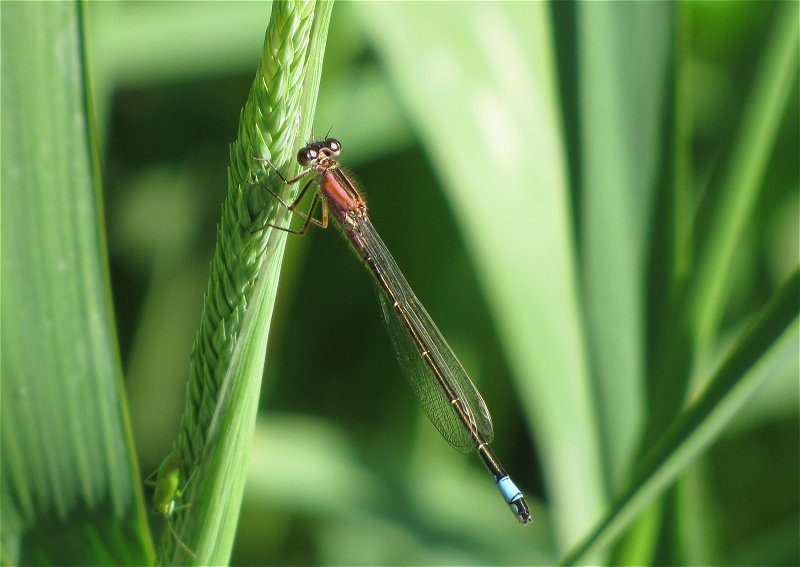
Female

Metallic green, with pale beige sides to the thorax. Distinctly thicker abdomen than male.
Behaviour
Weak flyer usually remaining close to emergent vegetation, rarely going far over water. Copulation usually takes place close to breeding site and last from 30 minutes to over an hour. Females usually arrive to oviposit in tandem with the male. Oviposits in to stems of emergent grasses, rushes, sedges and horsetails, usually above surface, but can submerge, including the male. Fairly sedentary and can be absent from seemingly good sites.
Habitat
Still or slow moving water such as ponds, bogs, ditches, canals and lake edges with dense emergent vegetation. Tolerates brackish and acidic water. Sensitive to excessive clearance of emergent vegetation.
Flight Period
 Status
Status
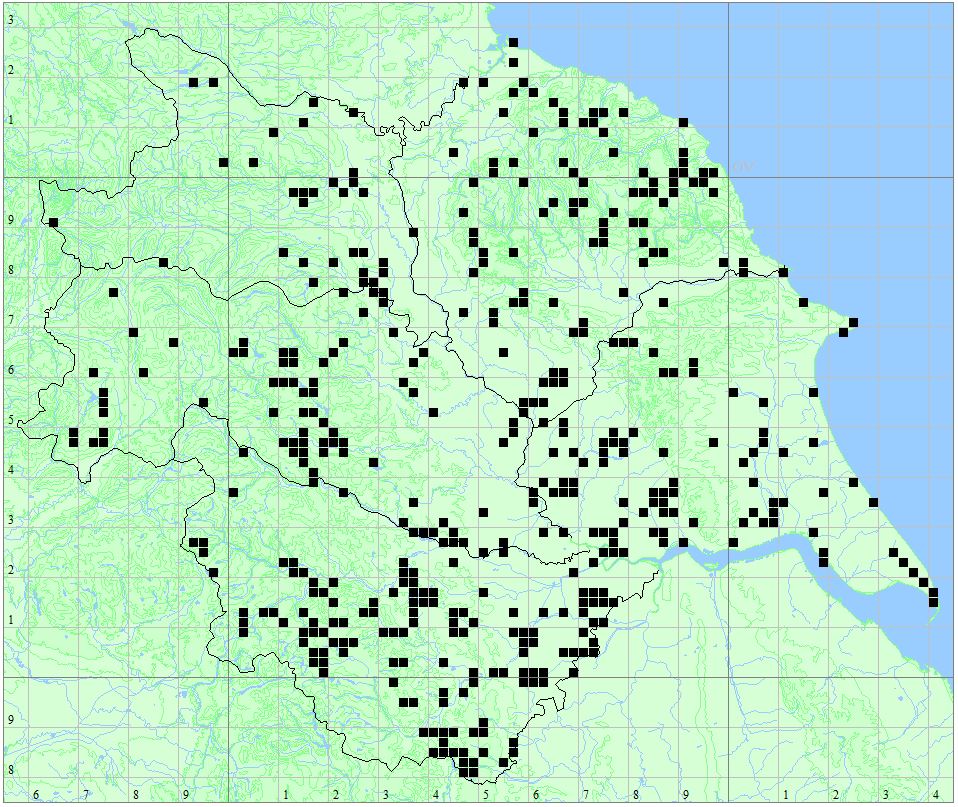
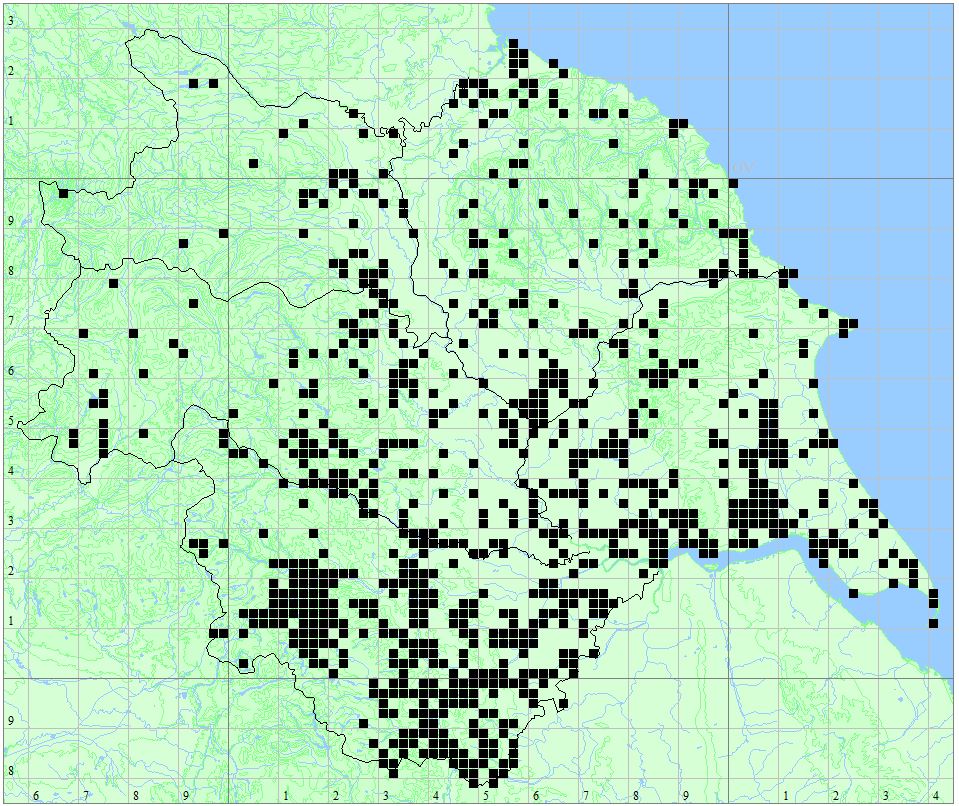
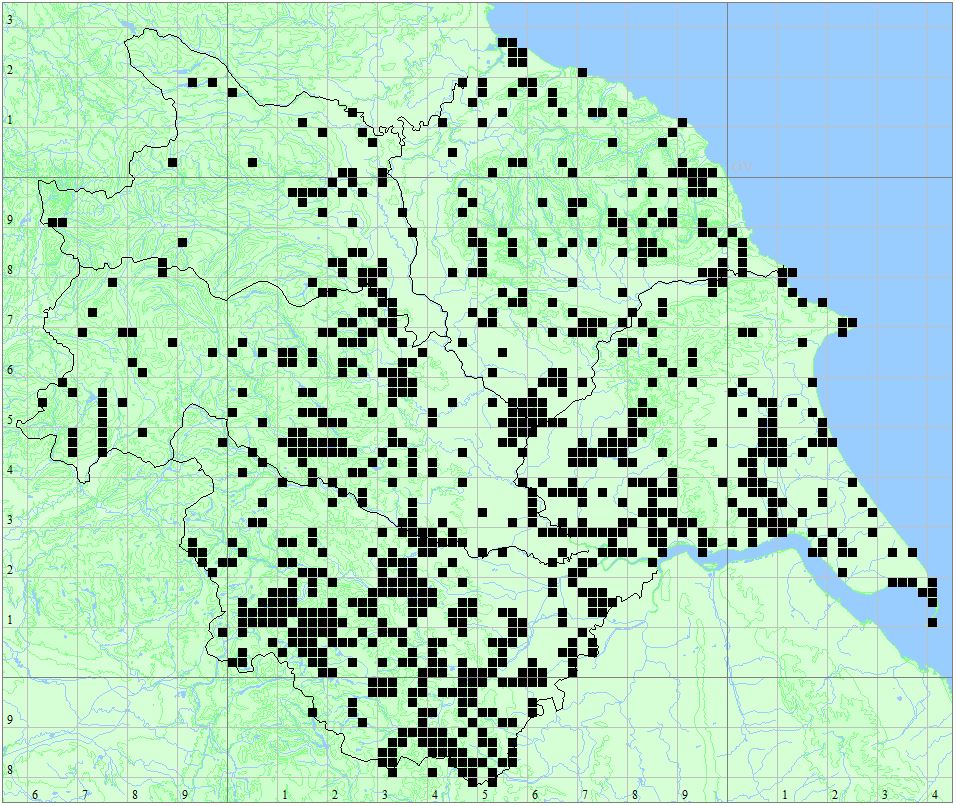
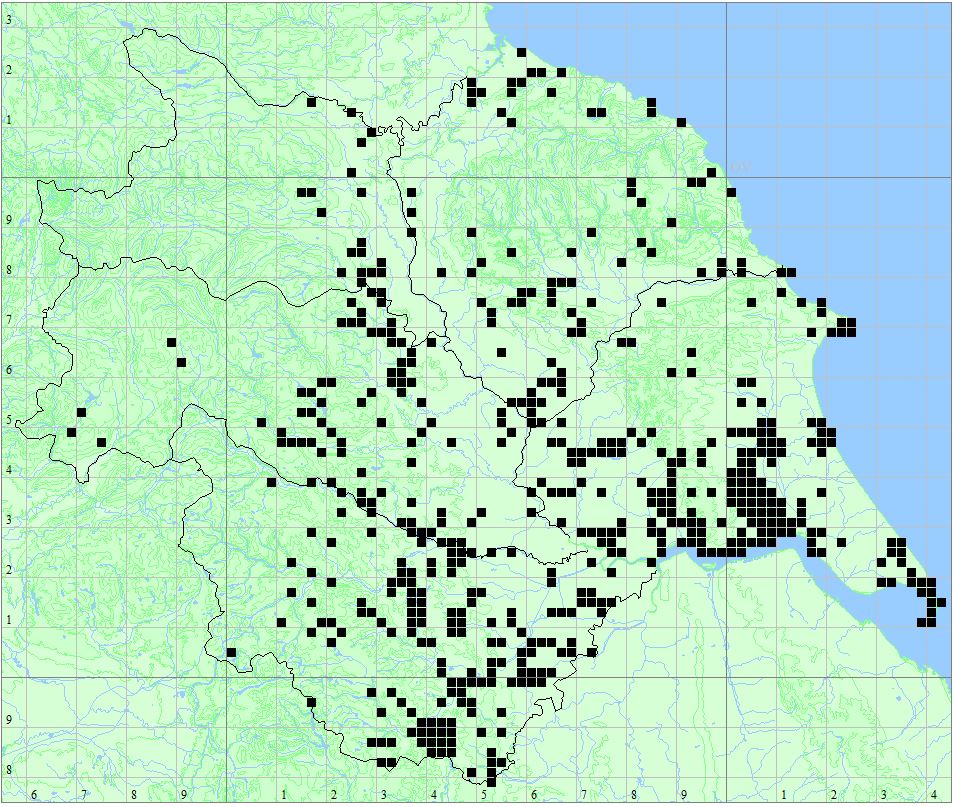
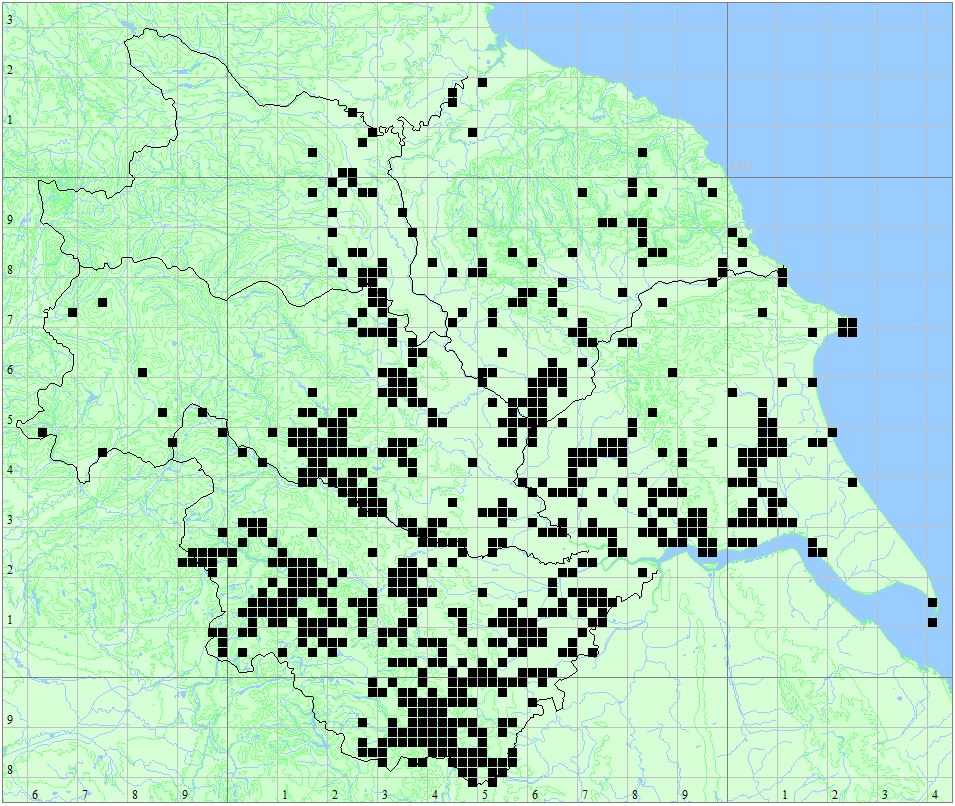
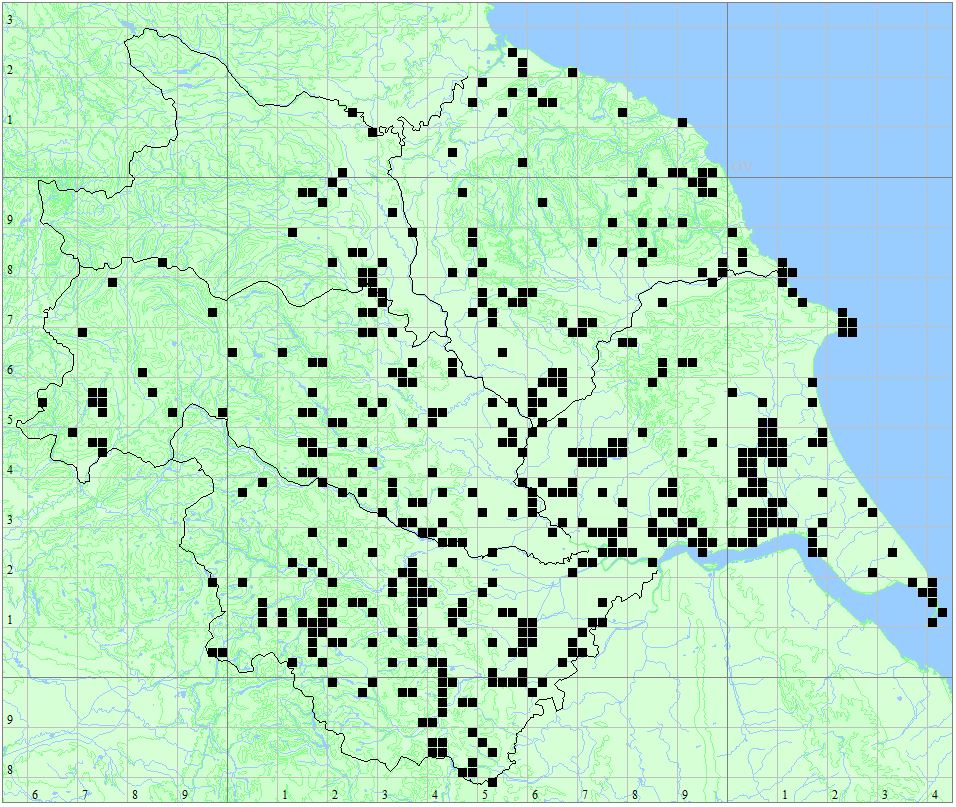
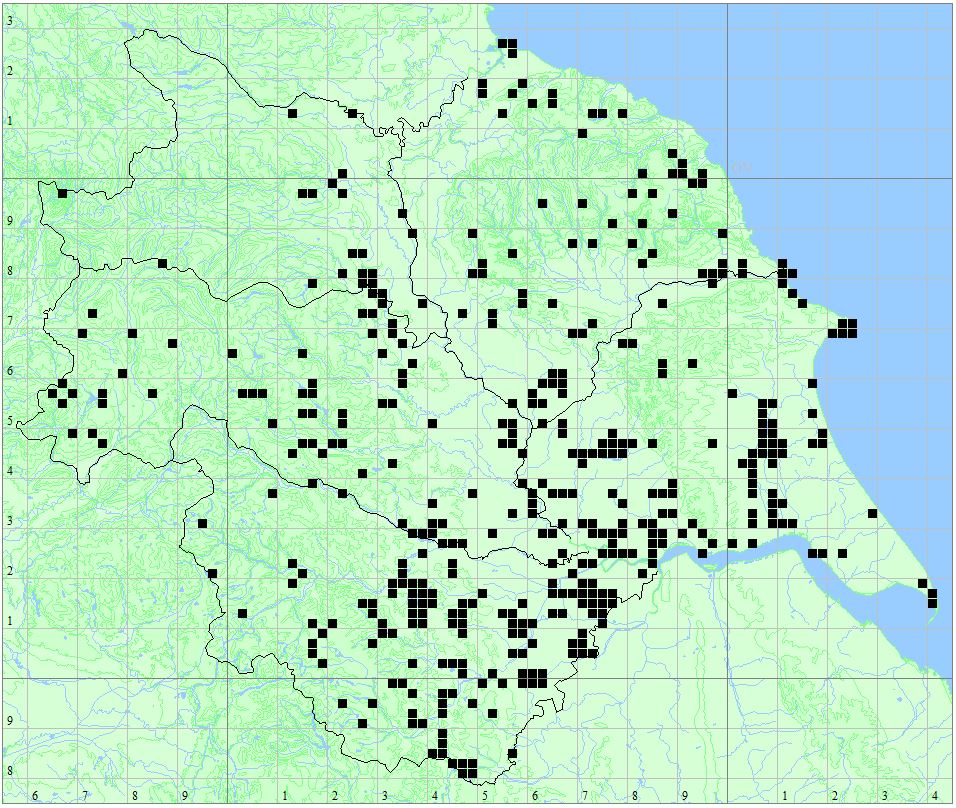
Found at many sites through all Vice-counties.
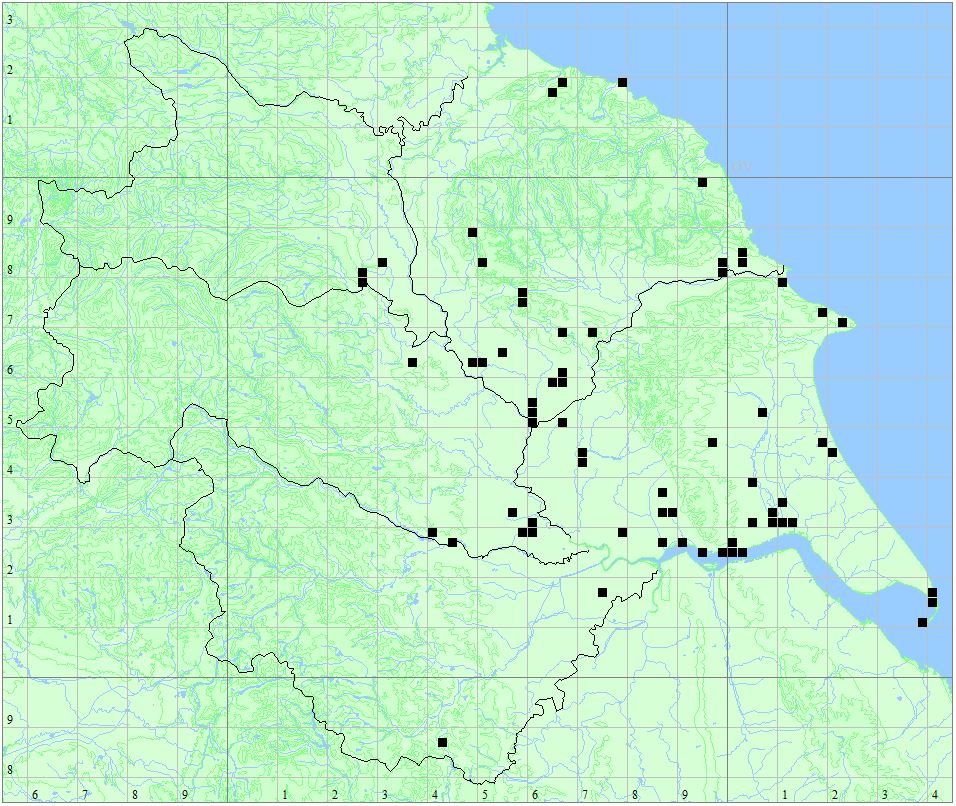
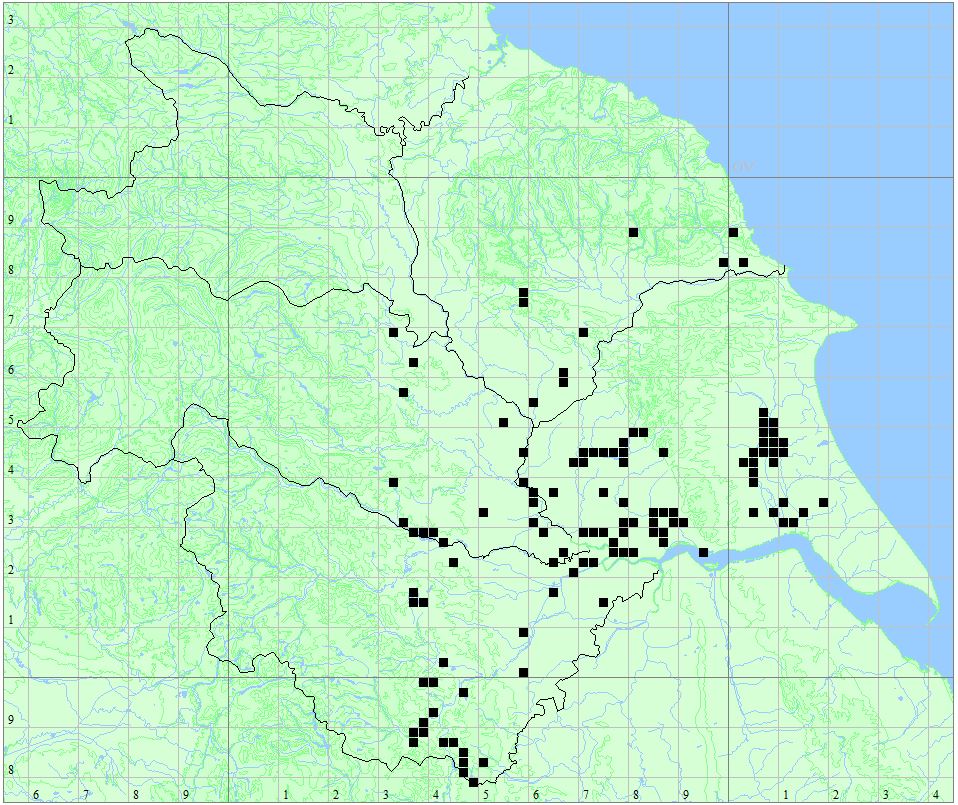
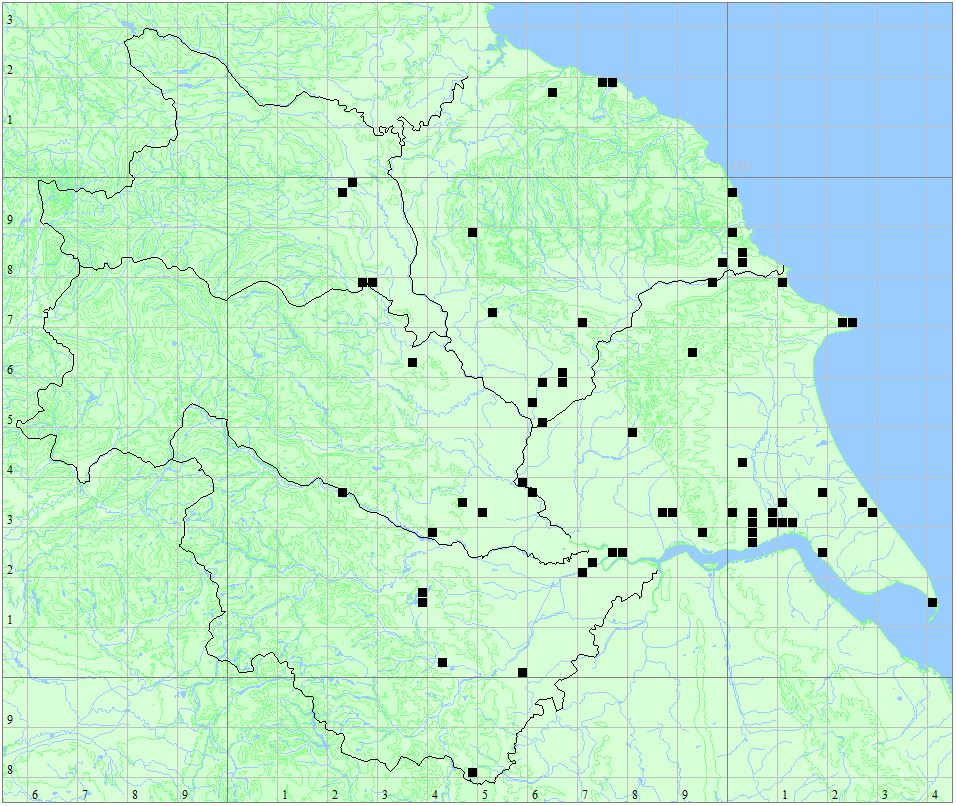
Distribution Map
Locations
- Rodley Nature Reserve
- Moorgates Quarry LNR
- Thorne Moors – Humberhead Peatlands NNR
- Thorpe Marsh
- Oakhill & Goole Brick Ponds
- Paull Holme Strays
- Treeton Dyke
- Rabbit Ings
- Walton Colliery Nature Park
- Pugneys Country Park
- The Yorkshire Arboretum
- Hurst Dam
- Nosterfield Local Nature Reserve
- Timble Ings
- Fairburn Ings
- Potteric Carr
- Dundale Pond
- The Tarn, Goathland
- Fen Bog
- Spurn Point
- Skipwith Common
- Saltmarshe Delph
- Pulfin and High Eske Nature Reserve
- Oak Road Lake, Hull
- North Cave Wetlands
- Filey Dams
- Eastrington Ponds
- Broomfleet Washlands
- Noddle Hill Nature Reserve
- Allerthorpe Common
- Tophill Low Nature Reserve